What Does Credits Mean In GPA?
Understanding the concept of credits in GPA is essential for students striving for academic excellence. In the realm of education, GPA (Grade Point Average) serves as a crucial metric that reflects a student's academic performance. Among various components that contribute to GPA, credits play a pivotal role. This article will explore what credits mean in GPA, how they are calculated, and their significance in a student's academic journey.
As a student, grasping the intricacies of credits can provide clarity in understanding how your academic efforts translate into your GPA. Whether you are in high school or pursuing higher education, knowing how credits work can help you make informed decisions regarding your course load and academic goals. Here, we delve deep into the definition of credits, their calculation, and their impact on your overall GPA.
This comprehensive guide aims to equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate your academic life effectively. We will also discuss best practices for managing credits to optimize your GPA and achieve your educational objectives. Let's begin by examining the fundamental aspects of credits and GPA.
Table of Contents
- What Are Credits?
- Importance of Credits in GPA
- How Credits Affect GPA Calculation
- Types of Credits
- Calculating GPA: The Role of Credits
- Strategies for Managing Credits Effectively
- Common Questions About Credits and GPA
- Conclusion
What Are Credits?
Credits are a standardized unit of measurement that reflect the amount of work required to complete a course in an educational institution. They are often associated with the number of hours a student spends in class and the amount of coursework they must complete outside of class. Typically, one credit corresponds to one hour of classroom instruction per week over a semester.
For example, a three-credit course usually involves three hours of class time per week, along with additional hours dedicated to studying, completing assignments, and preparing for exams. Understanding the concept of credits is crucial because they directly influence a student's GPA and academic standing.
The Role of Credits in Academic Programs
Credits are integral to various academic programs as they determine the progression towards graduation. Most degree programs require a specific number of credits to be completed within a designated timeframe. Here are some key points related to credits:
- Credits are used to measure a student's workload and progress in their academic journey.
- Each course typically has a predetermined credit value based on its complexity and time commitment.
- Accumulating the required number of credits is essential for graduation.
Importance of Credits in GPA
Credits hold significant importance when it comes to calculating a student's GPA. The overall GPA is computed by taking into account both the grades received in courses and the credit values of those courses. This means that a high-grade course with a greater number of credits will have a more substantial impact on a student's GPA than a low-grade course with fewer credits.
Impact of Credits on Academic Performance
Understanding how credits influence GPA can help students strategize their course selections effectively. Here are some key takeaways:
- Courses with higher credit values can significantly boost GPA if passed with good grades.
- Struggling with a high-credit course can lead to a more considerable drop in GPA compared to lower-credit courses.
- Balancing course load with credit values is essential for maintaining a healthy GPA.
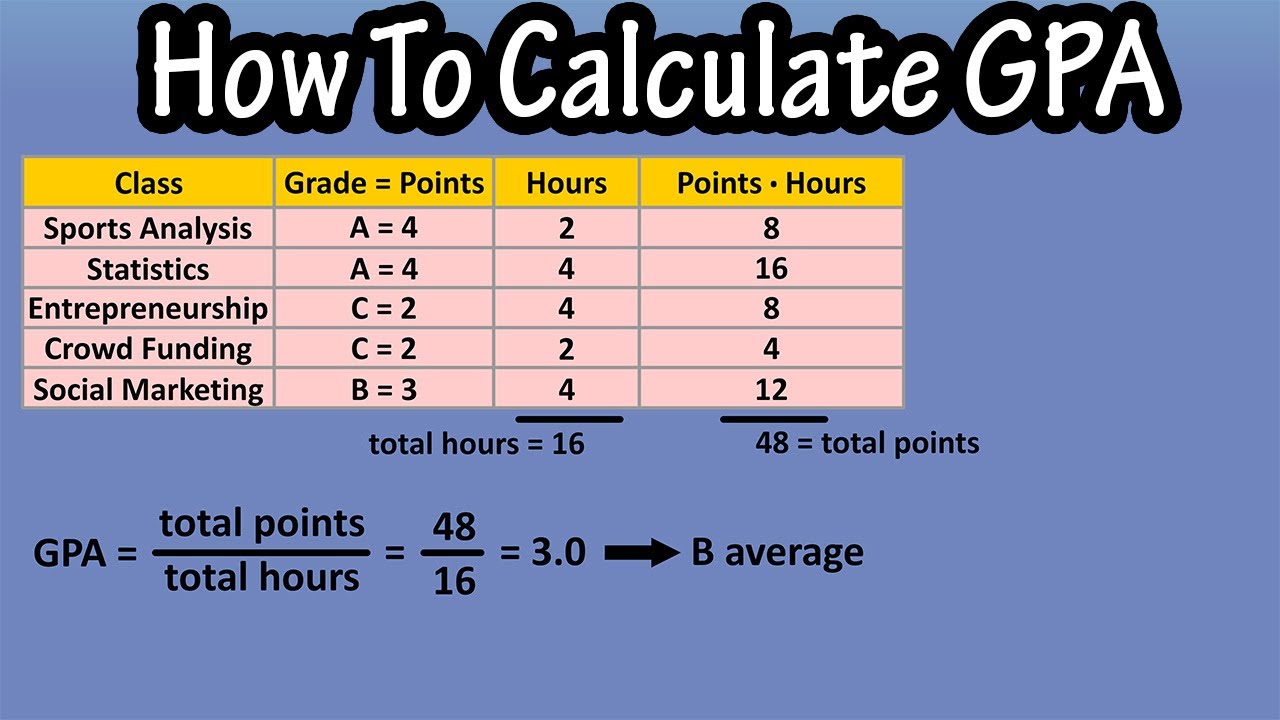
How Credits Affect GPA Calculation
The GPA is calculated by dividing the total grade points earned by the total credits attempted. The formula can be summarized as follows:
GPA = Total Grade Points / Total Credits Attempted
Grade points are assigned based on the grades received in each course, typically using a 4.0 scale. For example:
- A = 4.0 points
- B = 3.0 points
- C = 2.0 points
- D = 1.0 point
- F = 0 points
To calculate the total grade points for each course, multiply the grade points by the number of credits for that course. For instance, if a student earns an A (4.0) in a 3-credit course, their total grade points for that course would be:
4.0 (grade points) x 3 (credits) = 12 grade points
Types of Credits
There are various types of credits that students may encounter during their academic pursuits. Each type serves a different purpose and contributes uniquely to a student's academic profile. Here are the most common types:
1. Core Credits
Core credits are required courses that every student must complete as part of their degree program. These courses are designed to provide foundational knowledge and skills necessary for the field of study.
2. Elective Credits
Elective credits allow students to choose courses outside their core requirements. These courses can be related to the major or completely different subjects, providing students with an opportunity to explore diverse interests.
3. Transfer Credits
Transfer credits are awarded to students who have completed courses at another institution and wish to apply those credits toward their current program. Accepting transfer credits depends on the policies of the receiving institution.
4. Advanced Placement (AP) Credits
Advanced Placement credits are earned by high school students who take AP courses and score well on standardized exams. These credits can often be applied to college coursework, giving students a head start in their college education.
Calculating GPA: The Role of Credits
As previously mentioned, calculating GPA involves considering both grades and credits. Understanding the formula can help students monitor their academic performance effectively. Here’s a detailed breakdown of how to compute GPA:
- List all courses taken along with their respective credit values and received grades.
- Convert each letter grade into grade points based on the standard 4.0 scale.
- Multiply the grade points by the credits for each course to determine total grade points.
- Sum up all the total grade points and total credits attempted.
- Divide the total grade points by total credits to calculate GPA.
Strategies for Managing Credits Effectively
To optimize GPA and academic progress, students should consider the following strategies for managing credits:
- **Plan Your Course Load:** Be mindful of the number of credits you take each semester. Balance challenging courses with less demanding ones.
- **Consult Academic Advisors:** Seek guidance from academic advisors to ensure that your course selections align with your academic goals.
- **Make Use of Electives:** Utilize elective courses to explore interests that may enhance your major or provide valuable skills.
- **Stay Informed About Transfer Policies:** If considering transferring credits, understand your institution's policies to maximize credit transfer.
Common Questions About Credits and GPA
Here are some frequently asked questions regarding credits and GPA:
1. How many credits do I need to graduate?
The number of credits required for graduation varies depending on the degree program. Most undergraduate programs require around 120-130 credits.
2. Can I retake a course to improve my GPA?
Yes, many institutions allow students to retake courses to improve their grades. Check your school's policy on retaking courses and how it affects GPA calculations.
3. What happens if I drop a course?
Dropping a course may affect your credit load and GPA. Be sure to understand your institution's policies regarding dropped courses and their implications.
Conclusion
Understanding what credits mean in GPA is essential for academic success. Credits not only determine how GPA is calculated but also play a crucial role in fulfilling degree requirements. By managing credits effectively and leveraging the information provided in this article, students can enhance their academic performance and work towards their educational goals.
We encourage you to share your thoughts on this topic in the comments below. If you found this article helpful, consider sharing it with fellow students or reading more articles on our site to further your knowledge.
Article Recommendations
- Ray Epps
- Fighter Jet Joystick
- Napoleonynamite Actor
- Oskana Glamour
- Tudor Women S Fashion
- Green Evening Gown
- Tmc Blueberry
- The Matchmakers Asianwiki
- Nintendo Store Nyc
- Matt Dillon Wife