Understanding GCP Regions And Zones: A Comprehensive Guide
In the world of cloud computing, understanding GCP regions and zones is crucial for optimizing your applications. Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offers a variety of regions and zones to help you deploy your applications effectively and efficiently. By strategically selecting the right regions and zones, you can enhance performance, reduce latency, and ensure high availability for your services.
This article will delve into the intricacies of GCP regions and zones, providing you with essential insights and information to make informed decisions. We'll explore what regions and zones are, why they matter, and how to choose the best configuration for your needs. By the end of this guide, you'll have a solid understanding of how to leverage GCP's infrastructure to your advantage.
Whether you're a developer, architect, or business owner, the knowledge of GCP regions and zones is vital for scaling your applications and managing resources effectively. Let’s embark on this journey to explore the world of Google Cloud Platform!
Table of Contents
- Understanding GCP Regions
- Understanding GCP Zones
- Importance of Regions and Zones
- GCP Regions and Zones Overview
- How to Choose the Right Region and Zone
- GCP Regions and Zones for Specific Use Cases
- Data Sovereignty and Compliance
- Conclusion
Understanding GCP Regions
GCP regions are geographical locations where Google Cloud services are hosted. Each region consists of multiple zones, which are isolated locations within the region. When you choose a region, you are essentially selecting a physical location where your resources will reside.
Key Features of GCP Regions
- Multiple regions available globally.
- Each region is independent and has its own set of resources.
- Regions are designed for redundancy and disaster recovery.
Understanding GCP Zones
GCP zones are subdivisions within a region. Each zone is an isolated location with its own power, cooling, and networking to ensure that resources deployed in one zone are independent of resources in another zone within the same region.
Key Features of GCP Zones
- Zones provide higher availability and redundancy.
- Resources can be deployed across multiple zones for fault tolerance.
- Each zone is connected to other zones within the same region via high-speed network connections.
Importance of Regions and Zones
Understanding the importance of regions and zones is vital for optimizing your cloud deployment. The choice of region can significantly affect the performance, availability, and cost of your services.
Benefits of Choosing the Right Region and Zone
- Improved latency for end-users based on geographic proximity.
- Higher availability and disaster recovery options through multi-zone deployments.
- Compliance with local data regulations and standards.
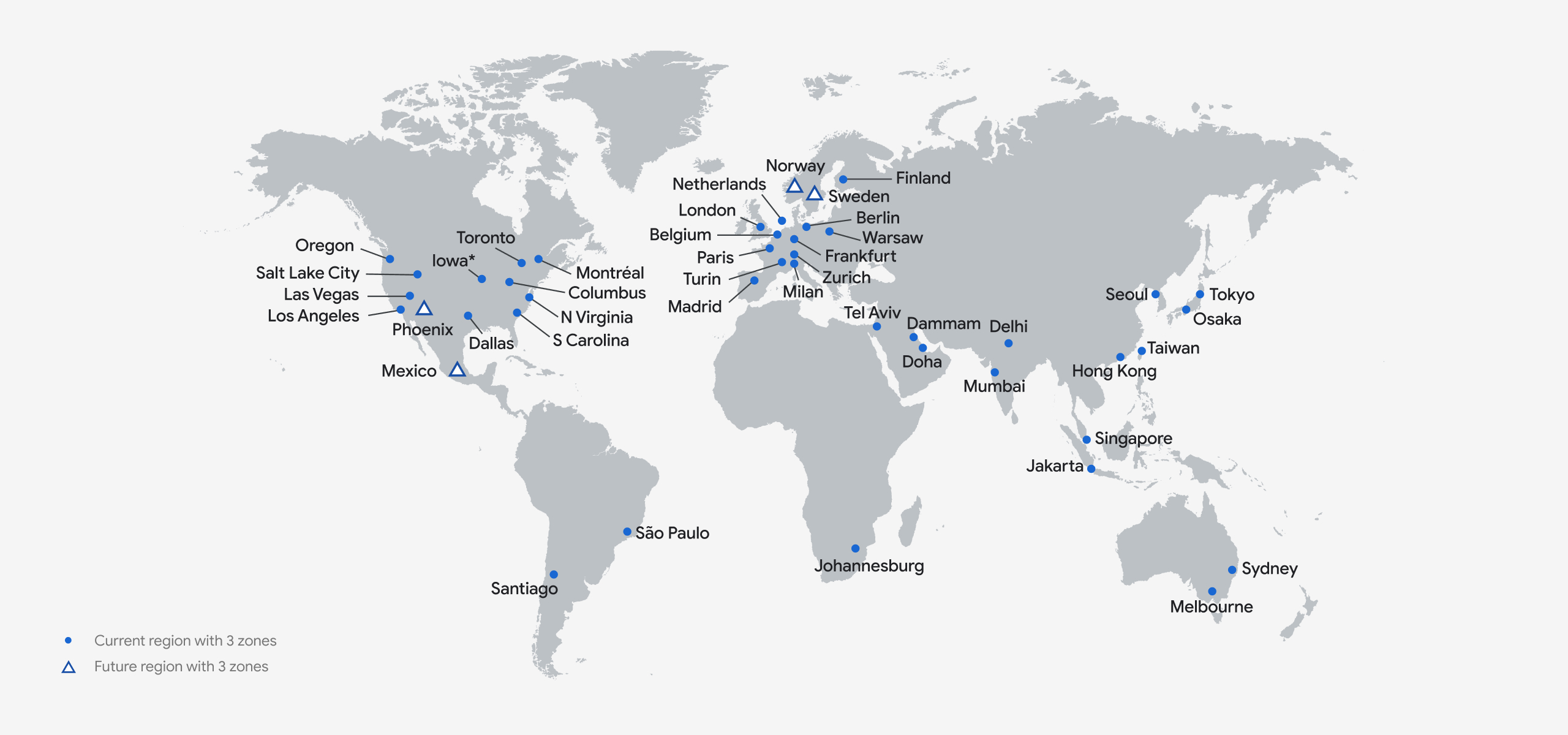
GCP Regions and Zones Overview
Google Cloud Platform currently offers numerous regions and zones worldwide, with each region containing multiple zones. As of October 2023, there are 37 regions and over 100 zones available globally.
List of GCP Regions and Zones
| Region | Available Zones |
|---|---|
| us-central1 | 3 (a, b, c) |
| us-east1 | 3 (b, c, d) |
| us-west1 | 3 (a, b, c) |
| asia-east1 | 3 (a, b, c) |
| europe-west1 | 3 (b, c, d) |
How to Choose the Right Region and Zone
Selecting the appropriate region and zone for your applications involves considering several factors, including latency, compliance, and disaster recovery strategies.
Factors to Consider
- Proximity to your target audience.
- Compliance with local data protection laws.
- Availability of specific services in the region.
- Cost of resources based on the region.
GCP Regions and Zones for Specific Use Cases
Different use cases may require different configurations of regions and zones. Let’s explore a few examples:
Use Case 1: High Availability Applications
For applications that require high availability, deploying resources across multiple zones within the same region is recommended. This setup ensures that if one zone experiences an outage, your application remains operational in another zone.
Use Case 2: Data Sovereignty
Businesses operating in regulated industries must consider data sovereignty when choosing a region. Selecting a region that complies with local data regulations can help avoid legal issues.
Data Sovereignty and Compliance
Data sovereignty is an essential consideration for organizations that handle sensitive information. By selecting the appropriate GCP region, businesses can ensure compliance with data protection laws, such as GDPR in Europe or HIPAA in the United States.
Compliance Best Practices
- Research local laws before selecting a region.
- Utilize GCP's compliance resources for guidance.
- Regularly review and update your compliance strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding GCP regions and zones is vital for optimizing your cloud infrastructure and ensuring high availability, performance, and compliance. By making informed decisions about where to deploy your resources, you can enhance your application's efficiency and mitigate risks.
We encourage you to explore GCP's offerings further and consider your specific needs when selecting regions and zones. If you have any questions or insights to share, please leave a comment below. Don't forget to share this article with others who might benefit from this information!
Thank You for Reading!
We hope you found this article on GCP regions and zones informative and helpful. Be sure to check back for more articles and resources related to cloud computing and technology. Your journey to mastering cloud infrastructure starts here!
Article Recommendations
- How To Find Archived Chats On Whatsapp
- High Protein Smoothies Without Protein Powder
- New York State Education
- The Matchmakers Asianwiki
- Hilton Irvine Orange County
- Anant Real Name
- Charcoal Grill Chicken Wings
- Female Nakedness
- Phone Number For Mcdonald S Customer Service
- Ihad Kroeger Married