Exploring The Highest Clouds In The Sky: A Journey Into The Atmosphere
The highest clouds in the sky are a fascinating subject for both meteorologists and curious minds alike. These ethereal formations not only captivate our imagination but also play a crucial role in Earth’s weather and climate systems. In this article, we will delve into the types of clouds that occupy the upper reaches of our atmosphere, their characteristics, and their significance in the broader context of meteorology and climate science. Whether you are a student, a weather enthusiast, or simply someone who enjoys gazing at the sky, understanding these clouds will enhance your appreciation of our planet's atmospheric phenomena.
The atmosphere is divided into several layers, each with its own distinct characteristics, and the highest clouds are typically found in the troposphere and stratosphere. These clouds can reach altitudes of over 20,000 feet (6,000 meters) and are often associated with unique weather patterns and phenomena. In the following sections, we will explore the different types of high-altitude clouds, their formation processes, and the important roles they play in our environment.
So, fasten your seatbelts as we embark on this enlightening journey through the highest clouds in the sky, where science meets wonder and beauty.
Table of Contents
- 1. What Are High Clouds?
- 2. Types of High Clouds
- 3. Formation of High Clouds
- 4. High Clouds and Weather Patterns
- 5. The Role of High Clouds in Climate
- 6. Significance of High Clouds in Meteorology
- 7. Fun Facts About High Clouds
- 8. Conclusion
1. What Are High Clouds?
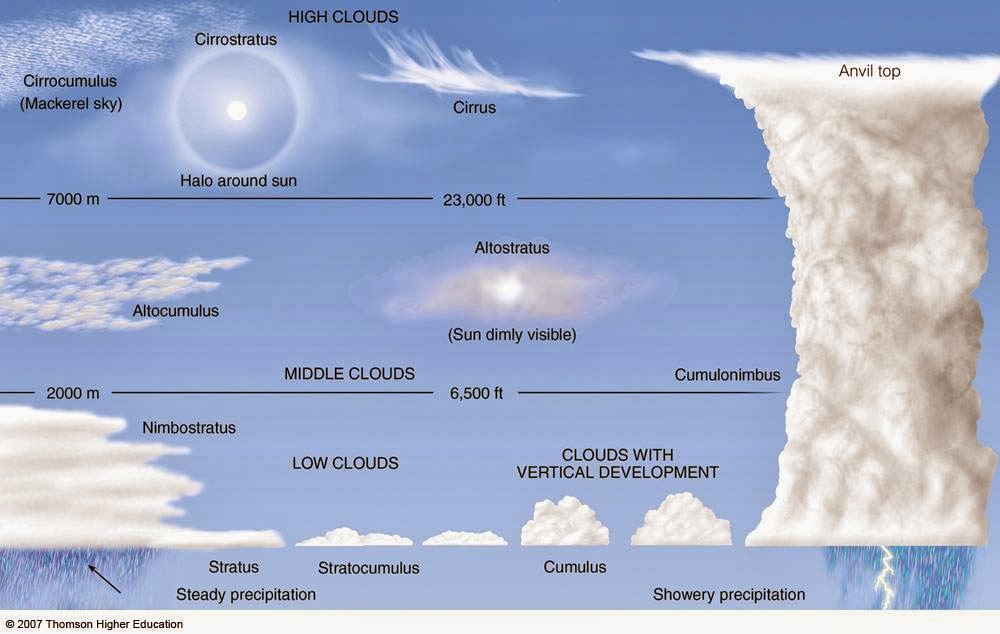
High clouds, also known as cirrus clouds, are those that form at altitudes of approximately 20,000 feet (6,000 meters) or higher. They are characterized by their thin, wispy appearance and are primarily composed of ice crystals. These clouds are often seen during fair weather but can also indicate an approaching storm, as they may signal moisture at high altitudes.
2. Types of High Clouds
High clouds can be categorized into three main types, each with distinct characteristics and formations. Understanding these types can help in predicting weather patterns and appreciating the beauty of our skies.
2.1 Cirrus Clouds
Cirrus clouds are the most well-known type of high cloud. They appear as thin, feather-like strands and are often white and wispy. Cirrus clouds form when water vapor in the upper atmosphere freezes into ice crystals. They are typically associated with fair weather, but their presence can also indicate that a change in the weather is on the way.
2.2 Cirrostratus Clouds
Cirrostratus clouds are a type of high cloud that forms a thin, ice-crystal layer covering the sky. These clouds can create a halo effect around the sun or moon, which is a result of the refraction of light through the ice crystals. Cirrostratus clouds often precede precipitation, signaling that rain or snow may be on the horizon.
2.3 Cirrocumulus Clouds
Cirrocumulus clouds are small, white patches of clouds that often appear in rows at high altitudes. They resemble ripples or waves and are usually formed from ice crystals. These clouds can indicate instability in the atmosphere and may suggest that a storm is approaching or that the weather will change.
3. Formation of High Clouds
The formation of high clouds is a complex process that involves the cooling of air and the presence of water vapor. When warm, moist air rises, it cools as it ascends. If the air cools to its dew point, condensation occurs, leading to cloud formation. In the case of high clouds, the temperatures are low enough that the water vapor condenses directly into ice crystals.
4. High Clouds and Weather Patterns
High clouds play a significant role in influencing weather patterns. Their presence can indicate changes in atmospheric conditions, as they often form ahead of a warm front. For instance, the appearance of cirrus clouds can signify that rain or snow may soon follow, making them essential for weather forecasting.
5. The Role of High Clouds in Climate
High clouds have a profound impact on the Earth's climate system. They can affect the amount of solar radiation that reaches the Earth's surface and can also influence the greenhouse effect. By trapping heat in the atmosphere, high clouds contribute to the overall warming of the planet, making their study crucial in understanding climate change.
6. Significance of High Clouds in Meteorology
The study of high clouds is vital for meteorologists and climate scientists. By monitoring these clouds, researchers can gain insights into weather patterns and climate trends. High clouds can also serve as indicators of larger atmospheric changes, allowing scientists to predict severe weather events more accurately.
7. Fun Facts About High Clouds
- High clouds are often composed of ice crystals, making them unique compared to lower clouds that primarily contain water droplets.
- Cirrus clouds can stretch across vast areas of the sky, but they are generally quite thin, allowing sunlight to penetrate through.
- The presence of cirrus clouds can be a sign of an approaching storm, as they often precede weather systems.
- High clouds can reflect sunlight back into space, helping to cool the Earth’s surface.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, the highest clouds in the sky are more than just beautiful formations; they are key players in our planet's weather and climate systems. Understanding their types, formation processes, and significance can deepen our appreciation for the atmospheric phenomena that surround us. We encourage you to observe the sky and take note of the clouds above you, as they can tell you a lot about the weather to come. If you found this article informative, please leave a comment, share it with others, or explore more topics on our site!
References
- National Weather Service. (n.d.). Cloud Types.
- American Meteorological Society. (n.d.). What Are Clouds?
- NASA. (n.d.). Clouds and Climate Change.
- Meteorological Society. (n.d.). The Role of Clouds in Climate.
Article Recommendations
- Harvard Egg And Feed
- Everything Is Fucked Book
- Elavil And Alcohol
- Ephesians 5 22 25
- Disney Junior
- Craig Smith
- Michael Kitchen
- Fighter Jet Joystick
- Csun Registration
- What Is An Ihome