Nervi Shiatik: Understanding The Sciatic Nerve And Its Importance
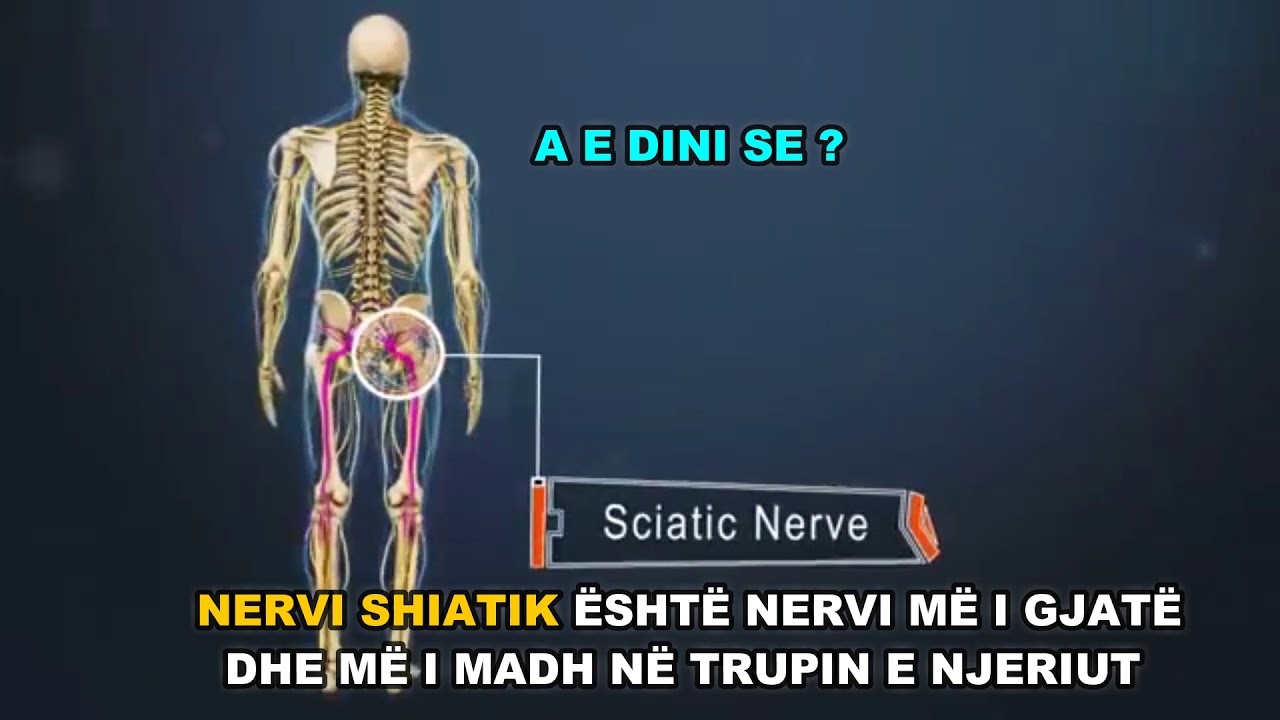
Nervi shiatik refers to the sciatic nerve, which is the largest nerve in the human body. This crucial nerve runs from the lower back down through the hips, buttocks, and legs, providing sensation and movement to various parts of the lower extremities. Understanding the anatomy and function of the nervi shiatik is essential for recognizing potential issues that can arise, such as sciatica, a condition characterized by pain radiating along the path of the nerve. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the nervi shiatik, its functions, and how it can affect our daily lives.
Many people experience discomfort or pain related to the sciatic nerve at some point in their lives. This can result from various factors, including injury, herniated discs, or even prolonged sitting. The symptoms of sciatic nerve pain can range from mild to severe, leading to decreased mobility and quality of life. Understanding the underlying causes and treatments available for nervi shiatik-related issues can help individuals effectively manage their condition and regain control over their lives.
As we explore the topic of nervi shiatik, we will address common questions regarding its anatomy, possible conditions related to it, and effective treatment methods. This comprehensive overview aims to provide readers with valuable insights into the importance of the sciatic nerve and how to maintain its health for a better quality of life.
What is the Anatomy of the Nervi Shiatik?
The nervi shiatik, or sciatic nerve, originates from the lumbosacral plexus, which consists of nerve roots L4 to S3. This long, thick nerve branches out into two major divisions: the tibial nerve and the common peroneal nerve. The anatomy of the sciatic nerve is crucial for understanding its function and the potential conditions that can arise when it is compromised.
How Does the Nervi Shiatik Function?
The primary role of the nervi shiatik is to provide motor function and sensory information to the lower limbs. It innervates various muscles in the back of the thigh, the entire lower leg, and the foot. Additionally, it supplies sensation to the skin of the posterior aspect of the leg and the entire foot. Understanding the nerve's function is essential for diagnosing and treating conditions like sciatica.
What Causes Sciatica and Nervi Shiatik Pain?
Sciatica is often caused by compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve. Some common causes of sciatica include:
- Herniated or bulging discs
- Spinal stenosis
- Piriformis syndrome
- Injury or trauma
- Pregnancy-related changes
What Are the Symptoms of Nervi Shiatik Issues?
The symptoms of conditions related to the nervi shiatik can vary widely from person to person. Common symptoms include:
- Sharp pain or a burning sensation in the lower back, buttocks, or legs
- Numbness or tingling in the affected leg
- Muscle weakness
- Pain that worsens with prolonged sitting or standing
- Pain that radiates down the leg
How Can Sciatica Be Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of sciatica typically involves a thorough medical history and physical examination. Healthcare providers may perform a series of tests to assess the patient's symptoms and determine the underlying cause of the pain. Some common diagnostic tools include:
- X-rays
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Computed tomography (CT) scans
- Nerve conduction studies
What Are the Treatment Options for Nervi Shiatik Issues?
Treatment for conditions related to the nervi shiatik may vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the symptoms. Common treatment options include:
- Physical therapy and exercises
- Medications such as anti-inflammatories or muscle relaxants
- Injections, such as corticosteroid injections
- Alternative therapies, including acupuncture or chiropractic care
- Surgery, in severe cases
How Can You Prevent Nervi Shiatik Issues?
Preventing issues related to the nervi shiatik involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and being mindful of posture and body mechanics. Some helpful tips include:
- Practicing good posture while sitting and standing
- Incorporating regular exercise and stretching into your routine
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing
- Using proper lifting techniques to avoid injury
What Should You Do If You Experience Sciatica Symptoms?
If you experience symptoms related to the nervi shiatik, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes and help prevent the worsening of the condition. Managing pain and restoring function should be the primary goals of treatment.
Conclusion: Understanding and Managing Nervi Shiatik
In conclusion, the nervi shiatik plays a vital role in the overall function of the lower body. Understanding its anatomy, function, and the potential issues that can arise is crucial for maintaining optimal health. By being proactive about prevention and seeking timely treatment, individuals can manage their symptoms effectively and improve their quality of life.
Article Recommendations
- Anant Real Name
- Aayushi Verma
- Tudor Women S Fashion
- Keri Russell And Kurt Russell Related
- Yvonne Elliman
- Does Ava Max Have A Husband
- Global Stability
- Are Keri Russell And Kurt Russell Related
- Evergreen Laundromat
- New York State Education