Understanding Glutamine Synthesis: A Comprehensive Guide
Glutamine synthesis is a critical biochemical process that plays a pivotal role in various metabolic functions within the human body. This amino acid, known for its significant contribution to protein synthesis, is essential for maintaining cellular health and supporting various physiological processes. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of glutamine synthesis, exploring its significance, mechanisms, and implications for human health.
As the most abundant free amino acid in the bloodstream, glutamine serves as a vital nitrogen donor and plays a crucial role in synthesizing nucleotides, which are the building blocks of DNA and RNA. Understanding how glutamine is synthesized and utilized in the body can provide valuable insights into its importance in nutrition, exercise, and overall health.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we will discuss the biochemical pathways of glutamine synthesis, the factors influencing its production, and its role in various physiological processes. Whether you're a student of biochemistry, a healthcare professional, or simply someone interested in nutrition and health, this article aims to provide you with a thorough understanding of glutamine synthesis.
Table of Contents
- What Is Glutamine?
- Biochemical Pathways of Glutamine Synthesis
- Importance of Glutamine in Human Health
- Glutamine and Exercise Performance
- Dietary Sources of Glutamine
- Glutamine Supplementation: Pros and Cons
- Consequences of Glutamine Deficiency
- Conclusion
What Is Glutamine?
Glutamine is classified as a non-essential amino acid, meaning that the body can synthesize it under normal conditions. It is particularly abundant in the muscles and serves multiple functions, including:
- Protein synthesis
- Serving as a nitrogen donor for nucleotide synthesis
- Supporting immune function
- Regulating acid-base balance in the kidneys
Glutamine: A Key Player in Metabolism
In the context of metabolism, glutamine plays a crucial role in nitrogen metabolism. It helps to transport ammonia, a byproduct of protein metabolism, from peripheral tissues to the liver, where it can be converted into urea and excreted. This process is essential for maintaining nitrogen balance in the body.
Biochemical Pathways of Glutamine Synthesis
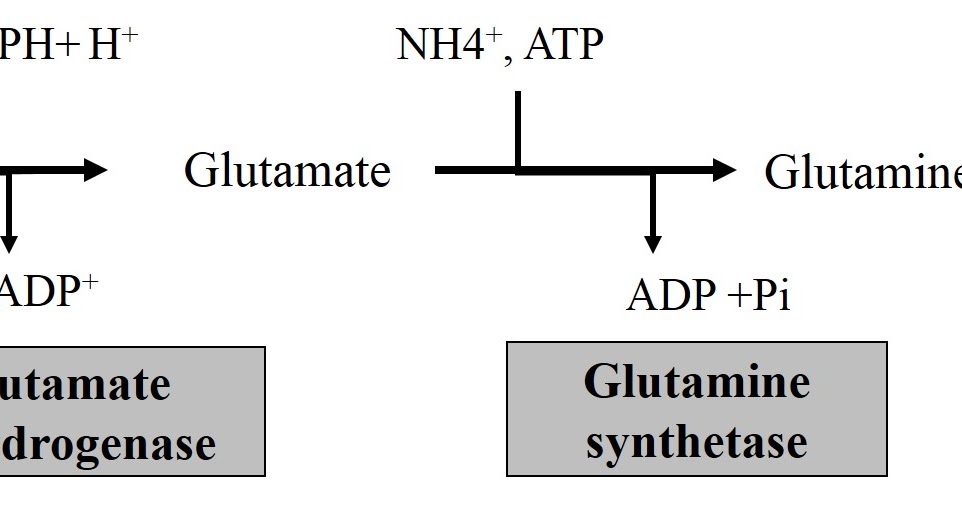
Glutamine is synthesized primarily from glutamate through the action of the enzyme glutamine synthetase. This reaction requires ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and ammonia (NH3). The overall reaction can be summarized as follows:
Glutamate + Ammonia + ATP → Glutamine + ADP + Pi
Role of Glutamate in Glutamine Synthesis
Glutamate, the precursor for glutamine, is also a crucial amino acid in its own right. It is involved in various metabolic pathways, including:
- Neurotransmission
- Energy production
- Protein synthesis
Importance of Glutamine in Human Health
Glutamine is vital for several physiological functions, including:
- Supporting immune system function
- Promoting gut health by serving as a primary fuel source for enterocytes (intestinal cells)
- Stimulating the secretion of growth hormones
Glutamine and Immune Function
During periods of stress, such as illness or intense exercise, the demand for glutamine increases. Adequate levels of glutamine can help support immune response and reduce the risk of infections.
Glutamine and Exercise Performance
For athletes and individuals engaged in intense physical training, glutamine may have performance-enhancing effects. Some potential benefits of glutamine supplementation in the context of exercise include:
- Reducing muscle soreness
- Enhancing recovery
- Supporting muscle growth
Research on Glutamine and Exercise
Several studies have examined the effects of glutamine supplementation on exercise performance and recovery. While results are mixed, some research suggests that it may help reduce muscle breakdown and support recovery after intense workouts.
Dietary Sources of Glutamine
Glutamine can be obtained from dietary sources, particularly high-protein foods. Some rich sources of glutamine include:
- Meat (beef, pork, chicken)
- Fish
- Dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese)
- Nuts and seeds
- Legumes
Glutamine in Plant-Based Diets
For individuals following a plant-based diet, sources of glutamine include:
- Tofu and tempeh
- Beans and lentils
- Spinach and cabbage
Glutamine Supplementation: Pros and Cons
While glutamine supplementation is popular among athletes and bodybuilders, it is essential to weigh the potential benefits against possible drawbacks. Some pros of glutamine supplementation include:
- Improved recovery time
- Enhanced immune function
- Support for gut health
However, there are also potential cons, such as:
- Lack of conclusive evidence for performance enhancement
- Possible gastrointestinal discomfort in some individuals
Consulting Healthcare Professionals
Before considering glutamine supplementation, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional, particularly for individuals with underlying health conditions or those taking medications.
Consequences of Glutamine Deficiency
While the body can produce glutamine, certain conditions may lead to decreased levels, including:
- Severe stress (e.g., surgery, trauma, infection)
- Intense physical training
- Malnutrition
Consequences of glutamine deficiency may include:
- Weakened immune response
- Increased risk of infections
- Gastrointestinal issues
Conclusion
In summary, glutamine synthesis is a vital process that has far-reaching implications for human health. Understanding its biochemical pathways, importance in metabolic functions, and potential benefits for exercise performance can help individuals make informed decisions regarding their nutrition and supplementation strategies. If you're considering incorporating glutamine into your diet, be sure to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure it aligns with your health goals.
We invite you to leave your thoughts or questions in the comments below and share this article with others who may find it helpful. For more articles on nutrition and health, be sure to explore our website.
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to seeing you again soon!
Article Recommendations
- Manila Airport Money Changer
- Flippin Jacks Ames
- Gale Boeticher
- Napoleonynamite Actor
- Montana State University Football
- Does Ava Max Have A Husband
- Weather Biloxi Ms
- Tick In Korean
- Line Dancing In Naples Fl
- Zachry